https://www.ikarussecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/BSI-DSZ-BSZ-0021-2025_IT-Sicherheitszertifikat_eng12019.png
753
752
IKARUS
https://www.ikarussecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/IKARUS-Security-Software-4-1.png
IKARUS2026-02-02 16:12:312026-02-02 16:18:51BSI-certified EDR agent for HarfangLab Guard feat. IKARUS
https://www.ikarussecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/BSI-DSZ-BSZ-0021-2025_IT-Sicherheitszertifikat_eng12019.png
753
752
IKARUS
https://www.ikarussecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/IKARUS-Security-Software-4-1.png
IKARUS2026-02-02 16:12:312026-02-02 16:18:51BSI-certified EDR agent for HarfangLab Guard feat. IKARUSAlthough a company was using a reliable email security solution, unwanted emails kept appearing in users’ inboxes. After a short investigation, the cause was quickly found: Port 25 was not restricted in the firewall.
Attackers were able to deliver emails directly to the internal mail server — bypassing the email gateway entirely. As a result, unwanted emails and attack attempts reached users despite the integrated security solution.
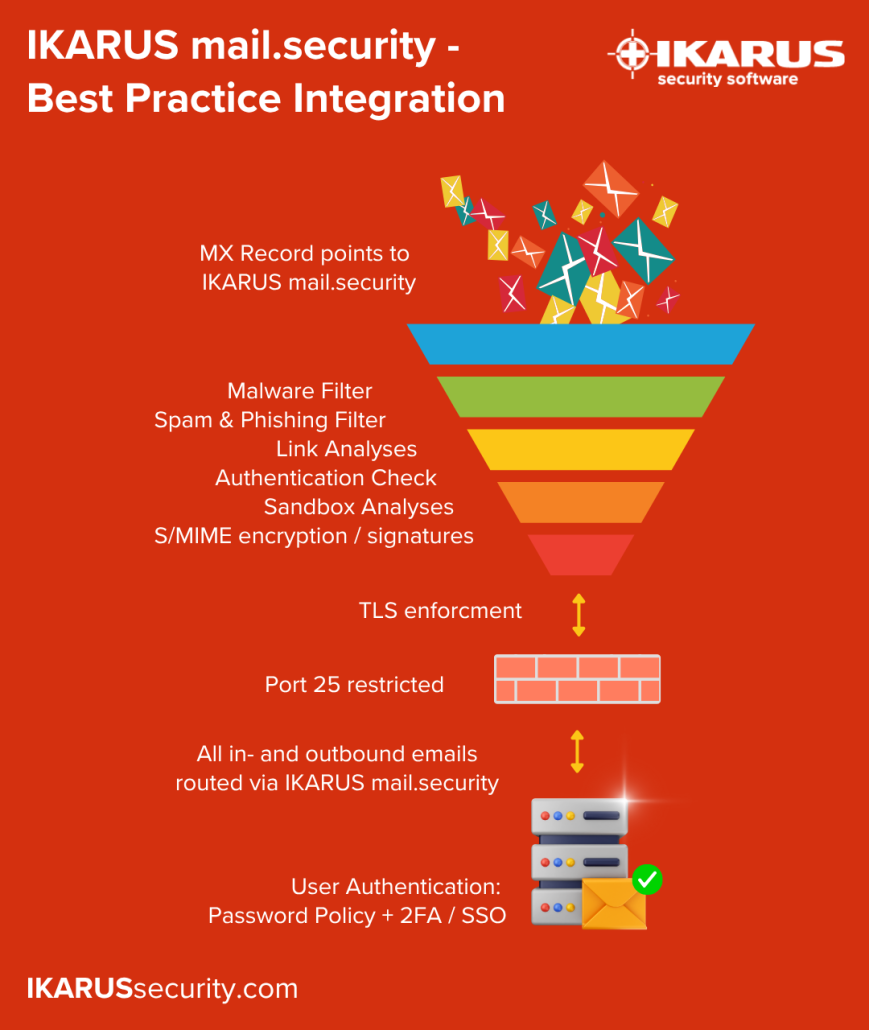
True email security requires seamless coordination between the firewall and the email protection system.
The role of the firewall
The firewall acts as the “bouncer” of the network. It controls which external connections are allowed in and which internal systems may communicate outward.
Inbound firewall rules:
- Ensure that no email reaches the mail server directly and bypasses email security.
- Best practice: SMTP connections to the mail server are allowed only from the email security gateway. Direct access from the internet is strictly blocked.
Outbound firewall rules:
- Prevent compromised internal systems from sending emails directly to the internet without being noticed.
- Best practice: SMTP (Port 25) should be used externally only by the mail server. All other systems must be blocked.
The role of email security
The email gateway filters and inspects every email before it reaches the internal mail server:
- Spam, phishing, and malware filtering
- URL defense
- Policy enforcement
- TLS encryption for secure transmission
Common mistakes in practice
1. Port 25 left open to everyone
Port 25 is the classic SMTP port for mail traffic between mail servers on the internet. If it remains open to internal clients or systems, multiple risks arise:
- Bypassing email security: Attackers or compromised systems can send emails directly to external recipients or to the internal mail server — without any threat inspection.
- Abuse for spam distribution: Malware on a client can use Port 25 to send spam or malicious content in bulk. The company’s IPs may quickly end up on blacklists.
- Direct attacks on internal mail servers: Open ports allow attackers to bypass the email security solution and exploit vulnerabilities on the mail server.
Best practice: Port 25 should be open only for the email security gateway. All other systems must be blocked.
2. Incorrect MX records
MX entries in DNS define where emails for a domain should be delivered. If they do not exclusively point to the email security gateway, external senders can deliver emails directly to the internal mail server — bypassing protection.
Best practice: Always configure MX records so that all incoming emails for all domains are routed through the gateway first.
3. Misconfigured clients – using Port 25 instead of submission
Many email clients use Port 25 by default for sending emails. However, this port is intended only for communication between mail servers. Clients should use dedicated, secure ports instead:
- Port 587 (Submission): Official standard for client email submission, using STARTTLS for encryption.
- Port 465 (SMTPS): Submission via a directly encrypted SSL/TLS connection.
If clients send via Port 25, the connection to the mail server may be unencrypted — allowing confidential data or credentials to be intercepted. Often, proper authentication is also missing, increasing the risk of misuse or attack.
Best practice: All clients must be configured to communicate with the mail server via submission ports (587 or 465). From there, email traffic must always be routed through the email security gateway.
4. TLS not enforced
Without TLS encryption, emails travel in plain text across the internet. This poses significant risks — even between the email gateway and mail server:
- Eavesdropping: Unauthorized parties can read the content, including confidential data.
- Manipulation: Messages can be altered in transit without the sender or recipient noticing.
- Identity theft: Credentials, signatures, or internal information can be intercepted and misused.
Best practice: Enforce at least TLS 1.2 and actively use domain-based TLS policies to prevent insecure fallback routes.
How attackers discover open ports
Cybercriminals specifically scan for vulnerabilities in company infrastructures. With freely available tools like nmap or Masscan, they can check within seconds whether Port 25 (SMTP) is open. Even without direct scanning, anyone can use services such as Shodan.io to search for open mail servers worldwide — including location and software details.
Many mail servers also reveal which software and version they are running during connection setup (“banner grabbing”).
If Port 25 is not strictly limited to the email security gateway, attackers can send emails directly to the internal mail server — bypassing protection. Spam, phishing, and malware then land unfiltered in users’ inboxes.
Conclusion
Email security does not end with deploying a gateway — it starts there. The correct interaction between firewall and email security ensures that:
- attacks cannot bypass the gateway,
- spam, phishing, and malware are reliably filtered,
- dangerous or manipulated URLs are detected, and
- emails are transmitted confidentially and tamper-proof.
Strict firewall control of Port 25 and enforced TLS encryption are key settings for ensuring reliable email protection.